IVF-ET Procedure
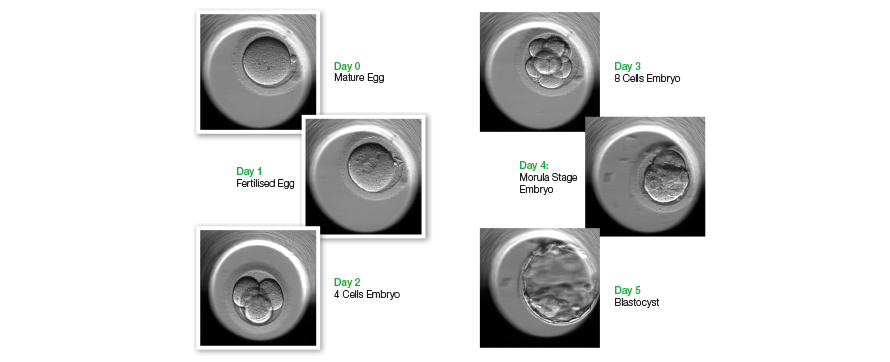
Normally, the egg and sperm meet at the fallopian tube (oviduct) where the fertilisation occurs. Then the fertilised egg (embryo) travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus, implants into the uterine wall and grows to pregnancy, if uterine conditions are favourable. IVF procedure is to assist in this process for the patients, whose fallopian tubes are blocked or for any other reasons that the sperm and egg cannot physically meet each other naturally. In fact, IVF refers to conventional in vitro fertilisation technique for patients with normal sperm parameters. The egg(s) are retrieved from the ovaries after controlled ovarian stimulation and ovulation induction. Eggs are cultured in a controlled environment (mimicking the human body temperature, humidity and oviductal fluid) in the IVF laboratory, the sperm will be added to the cultured dish containing eggs. The resulted embryos are transferred to the patient’s uterus on Day 2 to Day 5, or the longest may be up to Day 6.